1 Introduction
The purpose of this technical paper is to clarify the requirements for the application of aluminium cladding to air ducts, water pipes and refrigerant pipes with thermal insulation applied. The cladding provides protection to the thermal insulation from physical damage during the life of the installation.
An assessment has been carried out to identify all of the possible situations that air ducts, water pipes and refrigerant pipes can be in and what type of protective covering is required for each of these situations.
2 Current Situation
A standard specification for aluminium cladding is as follows:
JY50.1309 Protective Coverings
a) Protective coverings shall be installed on areas of insulation that are exposed to weather or subject to mechanical damage.
b) Insulation inside false ceilings and service ducts shall not require any finish.
c) Aluminium hammerclad 0.8mm thick cladding firmly secured with ‘pop’ rivets evenly spaced at 100mm centres shall be applied to insulation which is:
i) Visually exposed to view in public areas
ii) Exposed to view in back of house areas
iii) Located in plant rooms below a height of 2.5m above finished floor level.
d) Cladding shall be provided with means of removal for repair and maintenance.
This statement does not take the situation of occupancy and weather exposure criteria into account which may lead to having cladding in unnecessary areas such as risers or corridors.
A detailed assessment was carried out to clarify this.
1 Assessment Method
All of the spaces in the station were divided into three main locations:
- Back of House Areas
- Public Spaces
- External Spaces
Then four criteria were defined to take all of the possible situations into account, including:
- Exposure to weather or rain
- Exposure to view
- Being located in regularly occupied spaces
- Located at low level i.e. below a height of 2.5 meter above the finished floor.
The combination of the locations and the four criteria resulted in 48 different scenarios. Many of those scenarios are impossible in real life such as being exposed to weather in back of house areas. Therefore in the next step those scenarios were refined.
Then, the following rules were applied to make the list as relevant as possible:
- Services that are exposed to weather shall be clad.
- Services that are not exposed to view do not need cladding.
- In public spaces, all of the services exposed to view shall be clad.
For instance, if a service is exposed to weather then being exposed to view is not a concern anymore; therefore related scenarios can be removed from the list. Applying these rules resulted in a reduction to the unique scenarios that needed to be assessed. These are shown in Figure 1.
| Location |
Exposed to view |
Normally Occupied
Room |
Low Level* |
Aluminium Cladding Required? |
| Back of House |
|
|
|
Yes |
| |
|
|
Yes |
| |
|
|
Yes |
| |
|
|
No |
| |
|
|
No |
| |
|
|
No |
| |
|
|
No |
| |
|
|
No |
| Location |
Exposed to view |
Aluminium Cladding Required? |
| Public Spaces |
|
Yes |
| |
No |
| Location |
Exposed to rain |
Exposed to view |
Low Level* |
Aluminium Cladding Required? |
| External Spaces |
|
|
|
Yes |
| |
|
|
Yes |
| |
|
|
No |
| |
|
|
Yes |
* Services below a height of 2.5 meter above the finished floor are considered as low level.
Figure 1 – Aluminium Cladding Assessment Tables
2 Aluminium Cladding Requirement Flow Chart
The following flowchart, Figure 2, has been developed based on the Assessment Tables. It can be used to determine if aluminium cladding is required for a service.
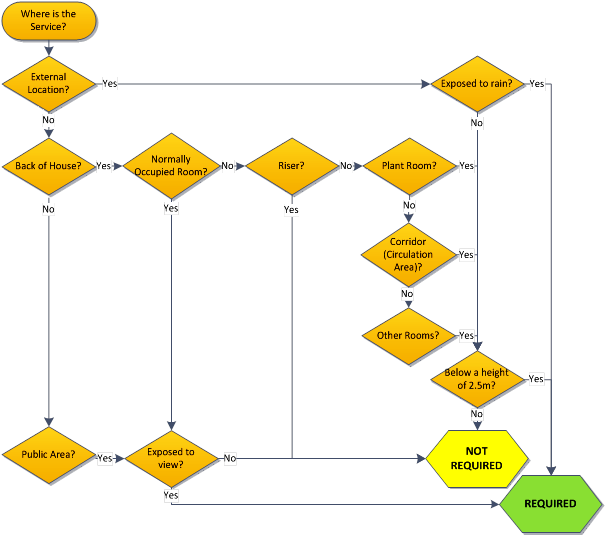
Figure 2 – Aluminium Cladding Flow Chart Assessment
3 Rain Cover Protection
In areas where services are exposed to rain, the risk of water penetration and damage to the duct or pipe and thermal insulation should be additionally assessed and appropriate means of water proofing provided.



