Project Initiation and Development
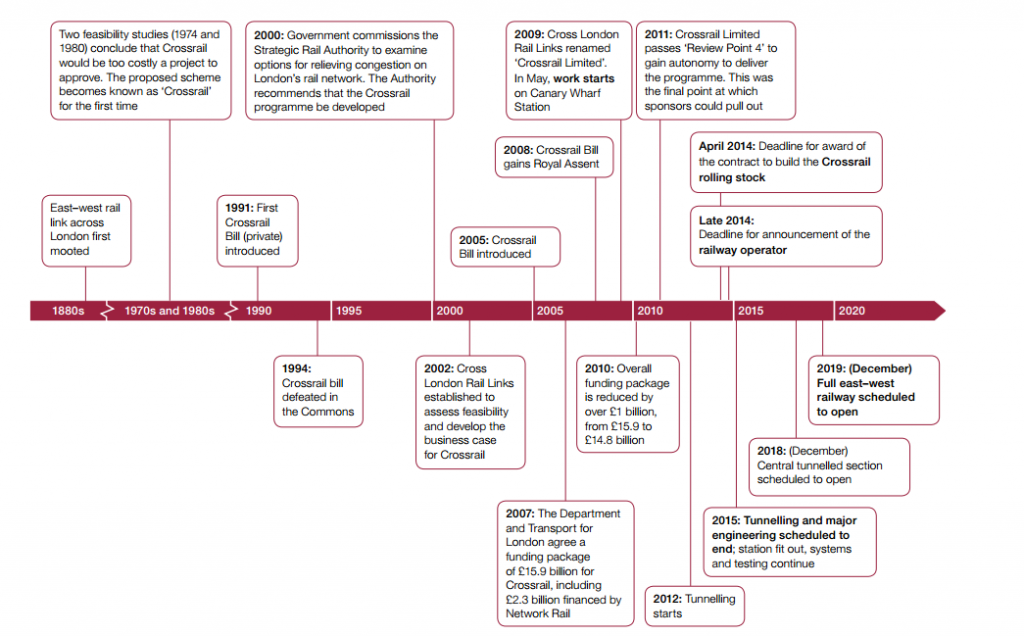
An east-west rail link across London was first mooted in the 1880s. More recent feasibility studies in 1974 and 1980 made little progress. A later attempt to promote the project on the back of the 1989 Central London Rail Study made more progress but failed when the Bill was defeated in the House of Commons and it was a further decade before the scheme was proposed in the Strategic Rail Authority’s London East West Study. This led to a joint venture with Transport for London (TfL) and a Bill for the current scheme was introduced to Parliament in 2005. By this time the growth of London was taking a severe toll on the existing London Underground system and the Central line in particular. London’s pre-eminence in the financial services boom of that period meant that the question of why Crossrail was needed turned to how and when? An extensive review of the options culminated in the Montague Report in 2004 concluding that the cost assumptions were realistic but there was doubt around the capacity to deliver a privately financed solution. The report pointed towards assembling an alternative funding and finance structure to enable the project to proceed.
In October 2007 the Department for Transport (DfT) and TfL agreed a Heads of Terms for a funding package of £15.9bn and designated Crossrail Limited as the delivery vehicle for the project. Construction work started at Canary Wharf in May 2009. As a result of extensive value engineering and risk mitigation Crossrail was able to retire £1.1bn of the funding package in 2010 leaving a revised budget of £14.8bn.
In publishing the PAC report in July 2014 committee member Richard Bacon MP cited Crossrail as a “textbook example of how to get things right” making strong reference to the structure and governance arrangements put in place between sponsors DfT and TfL and Crossrail Ltd. The Project Initiation and Development topic area examines through a number of subject areas how the Crossrail project developed from a compelling business case to a functioning delivery organisation.
Crossrail is the biggest infrastructure project in Europe and the largest infrastructure investment in the UK in a generation. The learning legacy paper on the Business Case describes how the case was made for such a huge investment and how the wider economic benefits of the scheme were assessed, the learning for future schemes being that crucial stakeholder support can be based on benefits which may not feature in the traditional cost-benefit analysis.
Prior to the Montague Report the Government’s preferred delivery model was a privately financed concession. When this proved to be unachievable the UK Treasury capped the contribution from the central exchequer at around a third of the overall cost requiring the remaining funding to be raised from the beneficiaries of the project. The learning legacy paper on Funding describes how the funding package was assembled.
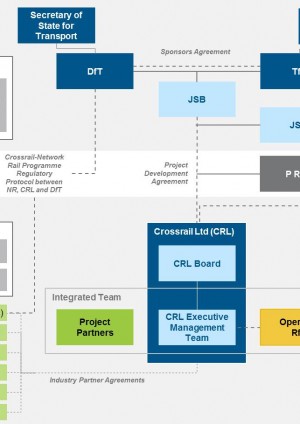
The funding arrangements created two separately accountable public sector sponsors – central government and London’s local government transport authority. Both sponsors were political bodies with separate and unaligned electoral timetables carrying the prospect of several combinations of political leadership over the 10 year project term. The learning legacy paper on Lessons Learned from Structuring and Governance describes the factors which shaped the delivery model structured around the creation of a sponsor organisation and a publicly owned and accountable SPV with an independent Board of Directors responsible for delivering the project.
| Summary |
Publication date |
Document Type |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The opening of the Elizabeth line on 24 May 2022 was a significant achievement for everyone involved in the delivery of Crossrail, including the Joint Sponsor team who oversaw the governance arrangements that supported the project through development, construction, commissioning and the successful transition into op...
|
05/04/2023 |
Journal Publication |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The Business Case for Crossrail had various iterations during the development, authorisation and delivery of the Crossrail Programme.
Cross London Rail Links Ltd published the Crossrail Economic Business Case in 2003. An independent review of the project was carried out for the DfT in 2004 by Sir Adrian Montague and ...
|
02/04/2023 |
Good Practice Document |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The Business Case for Crossrail developed along with the evolving scheme during the period until the Crossrail Bill was submitted, and was revised in 2010 alongside the Comprehensive Spending Review. Several innovations were incorporated most notably work to establish the Wider Economic Benefits of the scheme. This rep...
|
13/03/2018 |
Micro-report |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The Crossrail programme to deliver the Elizabeth line east–west railway across London, UK, was authorised by the Crossrail Act 2008. It was the culmination of 6 years of planning and development work by an organisation called Cross London Rail Links (CLRL), which was created for the purpose as a joint venture betwe...
|
22/08/2017 |
Journal Publication |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The £14.8 billion Crossrail project to deliver the new Elizabeth line east–west railway across London is the UK’s largest transport project. Getting it into reality was only possible through an innovative programme of finance, funding and value capture, which saw London business and future passenger revenues contr...
|
02/08/2017 |
Journal Publication |
Topic area: Project Initiation and Development The delivery model for Crossrail has proved successful and could form a template for other large and complex government-funded infrastructure projects. The independence and autonomy delegated to Crossrail Limited by sponsors, separating them from the delivery body, has provided an effective solution to support the real...
|
26/04/2016 |
Case Study |
Topic area: Innovation Programme The Crossrail innovation programme, at the time of its inception in 2012, focussed on generating innovation through sharing rather than providing a return on investment. To enable this a small pot of funding was created to trial ideas and to develop an innovators network that raised the bar for the industry. Once the...
|
22/03/2016 |
Research Paper |
Topic area: Sustainability Strategy The sustainability strategy for delivering the Crossrail programme sets out the key sustainability themes that are material to delivery of the project and identifies key performance indicators to be used to track performance. The strategy adopts a holistic approach, taking a balanced view on environmental, social and e...
|
26/02/2016 |
Good Practice Document |
Topic area: Regeneration The Property Impact Study was commissioned to understand the property market benefits arising in terms of market activity, value uplift and the development opportunities that Crossrail will create, unlock and support. It will be of interest to major project sponsor and client organisations wishing to demonstrate the re...
|
01/10/2012 |
Good Practice Document |